Introduction to Hull Designs for Large Powerboats
In this module, we’ll explore the various hull designs that are commonly used in large powerboats, typically those greater than 26 feet in length. Understanding hull design is crucial for making informed decisions about the type of boat that best suits your needs, whether you’re planning on cruising, fishing, or participating in other boating activities. Each hull design offers unique advantages and characteristics that affect performance, stability, and handling.
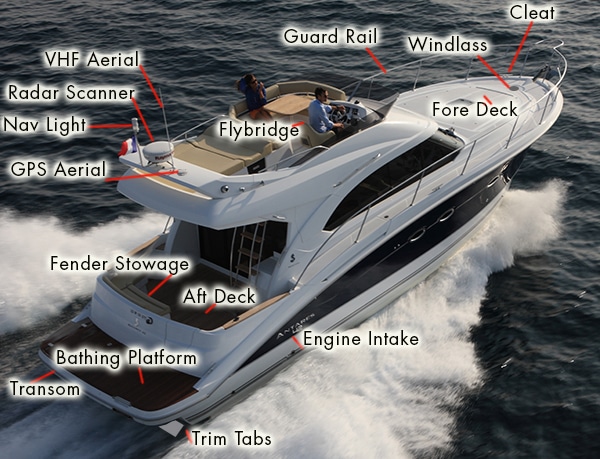
Here is a typical large recreational powerboat with some common names.
Types of Hull Designs
Deep-V Hull: Known for its sharp V-shaped cross-section, this design provides a smooth ride in rough waters by cutting through waves, making it ideal for offshore boating. Deep-V hulls tend to roll side to side when at rest even with small waves.
Modified-V Hull: A variation of the deep-V hull with a flatter bottom towards the stern, offering a balance between stability at rest and good handling in choppy conditions.
Catamaran Hull: Featuring two parallel hulls, this design offers exceptional stability, reduced drag, and a spacious deck, making it popular for both cruising and fishing.
Planing Hull: Designed to rise up and glide on top of the water at higher speeds, this hull is often used in speedboats and performance-oriented powerboats.
Displacement Hull: A design that moves through the water by displacing it (moving the water out of the way), offering a smooth ride and excellent fuel efficiency at lower speeds, typically found in trawlers and cruisers.
Semi-Displacement Hull: Combining elements of both displacement and planing hulls, this design offers a balance of speed and efficiency, suitable for long-distance cruising.
Following is an overview of these hull designs and discuss how they influence the performance and capabilities of large powerboats. Understanding these fundamentals will help you choose the right hull for your specific boating needs.